Overview
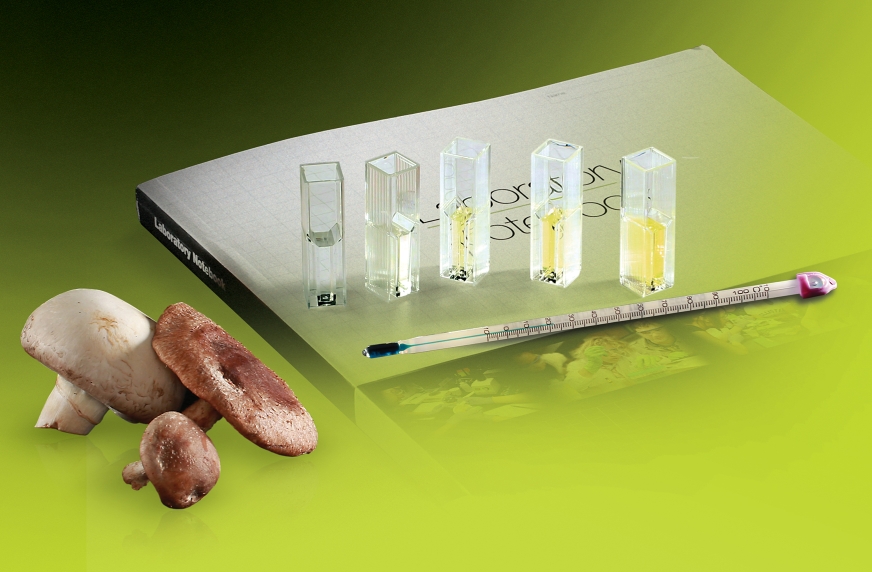
Reveal the power of enzyme kinetics by illustrating their function through the real-world application of biofuel production. The Biofuel Enzyme Kit measures the enzymatic activity of cellobiase (part of the cellulase family) and identifies the optimal conditions for the enzyme. The reaction of cellobiase breaking down cellobiose is important in the process of making cellulosic ethanol, which is an efficient, more sustainable fuel to replace petroleum. Students test and calculate the conversion rate of a sugar substrate (p–nitrophenyl glucopyranoside) to p–nitrophenol and glucose in the presence or absence of cellobiase.
Features and Benefits
- Guides instruction on enzyme kinetics and biofuel energy sources
- Contains no caustic reagents
- Enables both qualitative and quantitative measurements of reactions
After establishing the reaction rate in the presence of the enzyme, various conditions can be tested. Students can perform the following independent inquiries:
- Determine the effect of temperature on the reaction rate
- Determine the effect of pH on the reaction rate
- Determine the effect of enzyme concentration on the reaction rate
- Determine the effect of substrate concentration on the reaction rate
- Test the ability of mushroom extracts to increase the reaction rate
Background Information
Cellulosic ethanol is a biofuel derived from plant matter. Cellulose is a polysaccharide found in the cell walls of plants. The breakdown of cellulose into sugar is a multistep process that is facilitated by a family of enzymes called cellulases. Each cellulase has its own unique role in processing cellulose from a long strand of glucoses down to single units that can then undergo microbial fermentation to produce ethanol.
More Information
- One 45 min laboratory activity
- Provides sufficient materials for eight student workstations, up to four students per workstation
Specifications
(2–4 students per workstation)
Ordering
items
Use the filters below to refine results!