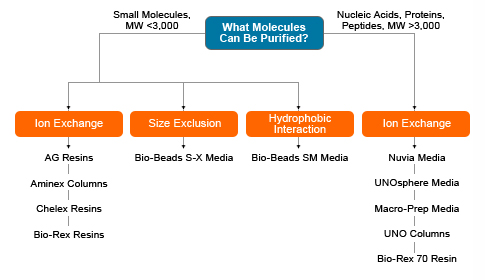
Ion exchange chromatography is a technique for separating compounds based on their net charge. Ion exchange chromatography media contain negatively or positively charged functional groups covalently bound to a solid support, yielding either a cation or anion exchanger, respectively. Charged compounds are adsorbed and retained by an ion exchanger having the opposite charge, whereas compounds that are neutral or have the same charge as the media pass through the void volume and are eluted from the column. The binding of the charged compounds is reversible, and adsorbed compounds are commonly eluted with a salt or pH gradient. Ion exchange media are available in various particle sizes, ionic forms, and purity ranges.
This section provides an overview of the selection of ion exchange chromatography media based on factors such as the isoelectric point (pI) of the compounds to be separated and the ionic form, porosity, and particle size of the media. The quick guide for media selection below is based on the specific technique used for separation — such as ion-exchange, hydroxyapatite, fluoroapatite, or affinity chromatography — and the various media available from Bio-Rad for these techniques. To determine whether ion exchange chromatography is the most suitable approach for your application and to learn about other chromatographic methods that may be applicable to your purification needs, visit our Chromatography page.
Related Topics: Affinity Chromatography, Size Exclusion Chromatography, Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography, Mixed-Mode Chromatography, Low Pressure Chromatography Systems and Medium Pressure Chromatography Systems.
Page Contents
| Suitability** | |||||
| Media Type | Packaging Format* |
Analytical Scale |
Pilot/ Preparative Scale |
Process Scale |
Application |
| Anion Exchange Chromatography Media | |||||
| AG 1 | B, GC | ++++ | ++ | + | Strong exchanger. Separation of low MW peptides, nucleotides, inorganic ions using different crosslinkages; high selectivity for anions such as chloride; gravity or low-pressure use |
| AG MP-1M | B, GC | ++++ | ++ + | + | Strong exchanger. Macroporous, equivalent to AG 1 for MW >1,000,000; gravity or low pressure use |
| Bio-Rex 5 and AG 4-X4 |
B, GC | ++++ | ++ | Weak exchanger. Used to remove organic acids from sugars; adsorption of mineral acids; gravity or low-pressure use | |
| UNO Q | MPC | ++++ | Strong exchanger. High-resolution biomolecule separation at high flow rates; pH stability 2–12 | ||
| Macro-Prep High Q |
B, C | +++ | ++++ | + | Strong exchanger. High-capacity biomolecule separation; unique surface chemistry allows contaminant removal; pH stability 1–10 |
| Macro-Prep 25 Q | B | ++++ | ++++ | + | Strong exchanger. Similar to Macro-Prep High Q but 25 μm particle size allows higher-resolution separation; unique surface chemistry allows contaminant removal; pH stability 1–10 |
| Macro-Prep DEAE | B, C | +++ | ++++ | + | Weak exchanger. High-capacity biomolecule separation; unique surface chemistry allows contaminant removal; pH stability 1–10 |
| UNOsphere Q | B, C | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | Strong exchanger. High-productivity, high-capacity biomolecule separation; pH stability 1–14 |
| Aminex | HPLC | ++++ | High-pressure separation of carbohydrates, sugars, and small organic molecules; delivers industry-standard performance (U.S. Pharmacopeia) | ||
| Cation Exchange Chromatography Media | |||||
| AG 50W | B, GC | ++++ | ++ | + | Strong exchanger. Lower degree of crosslinking, useful for peptide and nucleotide separation; higher crosslinkages useful for small peptide and metals separation or cation removal; gravity or low-pressure use |
| AG MP-50 | B, GC | ++++ | ++ | + | Strong exchanger. Macroporous equivalent to AG 50W for MW >1,000,000; gravity or low pressure use |
| Bio-Rex MSZ 501 | B | ++++ | ++ | ++ | Same as AG 50 but with more uniform bead size; large bead size (650 μm) makes it ideal for large-scale (column or batch) industrial applications |
| Bio-Rex 70 | B | ++++ | ++ | ++ | Weak exchanger. High capacity for high MW (>1,000,000) solutes; can be used for purification and fractionation of peptides, proteins, enzymes, and other cationic molecules. Amenable to large-scale purification |
| Chelex 100 | B, GC | ++++ | ++ + | + | Weak exchanger. Chelating resin removes metals and is suitable for PCR applications; can also be used for ultrapurification of buffers and ionic reagents; gravity or lowpressure use. Available in molecular biology and biotechnology grades |
| UNO S | MPC | ++++ | Strong exchanger. High-resolution biomolecule separation at high flow rates; pH stability 2–12 | ||
| Macro-Prep 25 S | B | ++++ | ++++ | + | Strong exchanger. Similar to Macro-Prep High S, but 25 μm particle size allows higher-resolution separation; unique surface chemistry allows contaminant removal; pH stability 1–10 |
| Macro-Prep High S |
B, C | +++ | ++++ | + | Strong exchanger. High-capacity biomolecule separation; unique surface chemistry allows contaminant removal; pH stability 1–10 |
| Macro-Prep CM | B | +++ | ++++ | + | Weak exchanger. High-capacity biomolecule separation; unique surface chemistry allows contaminant removal; pH stability 1–10 |
| UNOsphere S | B, C | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | Strong exchanger. High-capacity biomolecule separation; pH stability 1–14 |
| UNOsphere Rapid S | B, C | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | Strong exchanger. Similar to UNOsphere S but with enhanced chemistries to overcome the pH shift that occurs with conductivity transitions and faster equilibration times; pH stability 1–14 |
| Nuvia S | B, C | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | Strong exchanger. Similar to UNOsphere S but surface modification allows extremely high-capacity biomolecule separation; pH stability 1–14 |
* B, bottle; C, cartridge (1 ml or 5 ml); GC, gravity column; SC, spin column; HPLC, high-pressure column; MPC, medium-pressure column.
** +, low suitability; ++, moderate suitability; +++, suitable; ++++, high suitability.
Selection of an ion exchange chromatography support depends on the properties of the compounds to
be separated.
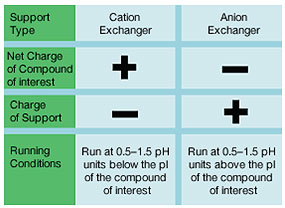
Isoelectric Point of the Compound — for amphoteric compounds, the pI of the compound and its stability at various pH values determine the separation strategy. At a pH above its pI, the compound of interest will be negatively charged; conversely, at a pH below its pI, the compound will be positively charged. Thus, when the compound is stable at a pH above its pI, an anion exchange support is used. Conversely, a cation exchange support is used when the compound is stable at a pH below its pI. The operating pH also determines the type of exchanger to use. A strong ion exchange support maintains its capacity over a wide pH range, whereas a weak one loses capacity when the pH no longer matches the acid dissociation constant (pKa) of its functional group.
Ionic Form of the Media — most ion exchange media are available in several ionic forms and may be converted from one form to another. The ionic form of a support refers to the counterion presently adsorbed onto the support's functional groups. Counterions exhibit specific selectivities for each support. The lower the selectivity of a counterion toward the support, the more readily it is exchanged for another ion of like charge. Consequently, the appropriate ionic form of the ion exchange media will depend on the relative selectivity of the sample ion to be adsorbed. In general, the ionic form should have a lower selectivity for the functional group than the sample ion, so that the sample ion will displace the counterion and be adsorbed onto the support. The sample ion can then be eluted by a second counterion with a higher selectivity for the support.
Media Porosity — the porosity of a support refers to the total pore volume within the matrix of the support; greater pore volume equals higher porosity. A very porous support may have either many small pores or a few large pores. The exclusion limit of a support is defined as the size of the largest compound that is able to enter the pores under a given set of conditions. Porous media with high exclusion limits are recommended for high-molecular weight compounds such as proteins, antibodies, and other biomolecules. Low- or high-porosity media with low exclusion limits are recommended for the separation of low-molecular weight compounds such as inorganic ions and organic acids. Some of the high-porosity media that Bio-Rad offers include the UNO family of ion exchange media, UNOsphere, Nuvia, Macro-Prep, and Bio-Rex 70 media. Low-porosity media include the AG and Chelex resins
Media Particle Size — particle size is measured in micrometers, with dry mesh or wet mesh designations. The wet particle diameter varies from support to support and depends on the ionic form resulting from differences in the hydration of the particles. Smaller particle sizes provide higher resolution and typically require lower operational flow rates; larger particle sizes yield lower resolution but can be operated at higher flow rates.
Bio-Rad also offers molecular-biology-and biotechnology-grade resins, free of endo- and exonuclease activity and ligase inhibitors as well as technical- and reactor-grade resins suitable for power plant deionization and large-scale cleanup of metal ions.