This section provides information on chemical transfection methods including liposome-meditated transfection, calcium phosphate, and viral mediated delivery.
Related Topics: Instrument-Based Transfection Methods, Posttransfection Analysis of Cells, and Cell Counting Methods.
Page Contents
| Method | Function | Recommended Cells | Products |
| Lipid-mediated | Uses lipids to cause a cell to absorb nucleic acids; transfer genetic material into the cell via liposomes, which are vesicles that can merge with the cell membrane | Immortal cells, adherent (attached), or suspension cells | TransFectin™ Lipid Reagent SiLentFect™ Lipid Reagent for RNAi |
| Viral vector (for example, retrovirus, lentivirus, adenovirus, or adeno-associated viruses) | Uses viral vectors to deliver nucleic acids into cells | Attached adherent cells, stem cells, primary cells |
| Advantages and Disadvantages of the Different Transfection Methods | ||
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| Lipid Mediated |
|
|
| Viral Mediated |
|
|
| Calcium Phosphate |
|
|
| DEAE-Dextran |
|
|
| Magnet Mediated |
|
|
The following table summarizes how common lipid and viral methods work.
| Protocols for Different Transfection Methods | |
| Lipid-Mediated | |
|
|
| Viral Mediated | |
RNA Viruses
Viral Transfection workflow. |
|
| Calcium Phosphate | |
|
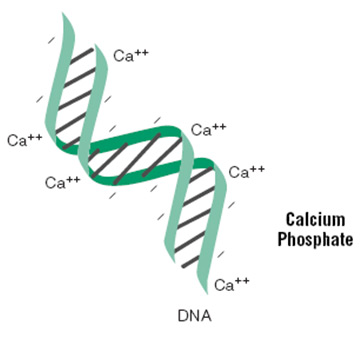
The protocol involves mixing DNA with calcium chloride, adding the mixture in a controlled manner to a buffered saline/phosphate solution, and allowing the mixture to incubate at room temperature. This step generates a precipitate that is dispersed onto the cultured cells. The precipitate is taken up by the cells via endocytosis or phagocytosis.
Intercalation of Ca++ ions. Protocol Solution A: DNA in calcium solution
|
|
| Cationic Polymers | |
|
Cationic polymers differ from cationic lipids in that they do not contain a hydrophobic moiety and are completely soluble in water. Given their polymeric nature, cationic polymers can be synthesized in different lengths, with different geometry (linear versus branched). The most striking difference between cationic lipids and cationic polymers is the ability of the cationic polymers to more efficiently condense DNA. There are three general types of cationic polymers used in tranfections:
Cationic polymers include polyethyleneimine (PEI) and dendrimers. |
|
| DEAE-Dextran | |
|
DEAE-dextran is a cationic polymer that tightly associates with negatively charged nucleic acids. The positively charged DNA:polymer complex comes into close association with the negatively charged cell membrane. DNA:polymer complex uptake into the cell is presumed to occur via endocytosis.
Protocol Solution A: DNA (~1–5 µg/ml) diluted into 2 ml of growth medium with serum containing chloroquine
|
|
| Activated Dendrimers | |
|
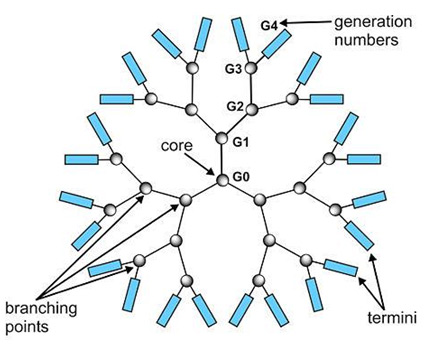
Positively charged amino groups (termini) on the surface of the dendrimer molecule interact with the negatively charged phosphate groups of the DNA molecule to form a DNA-dendrimer complex. The DNA-dendrimer complex has an overall positive net charge and can bind to negatively charged surface molecules on the membrane of eukaryotic cells. Complexes bound to the cell surface are taken into the cell by nonspecific endocytosis. Once inside the cell, the complexes are transported to the endosomes.
Dendrimer molecule. |
|
| Magnet-Mediated Transfection | |
|
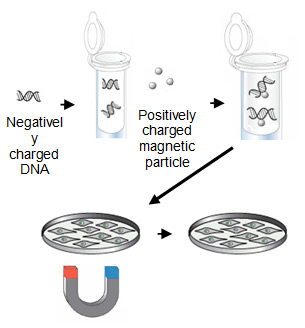
Magnet-mediated transfection uses magnetic force to deliver nucleic acids into target cells. Therefore, nucleic acids are first associated with magnetic nanoparticles. Then, application of magnetic force drives the nucleic acid-particle complexes towards and into the target cells, where the cargo is released.
Magnet-mediated transfection. |
The transfection protocol online library contains protocols obtained from the literature, developed by Bio-Rad scientists, or submitted by scientists like you. Browse protocols to view our library and find your starting point or submit a protocol by clicking the proper technology.
Related Content
Documents
TEST
| 6179 | Lipid Transfection Reagents Selection Guide | Click to download |