
On This Page |
Step 1 — Sample Collection | Step 2 — RNA Extraction | Step 3 — Analyzing RNA Quantity and Quality | Related Products | Resources |
RNA isolation is an important step in analyzing gene expression, which is a common application of RT-qPCR. The quantitative PCR (qPCR) process can be used to quantitate expression levels of genes in tissues or individual cells and detect gene activation or inactivation.
Gene expression requires RNA, which is reverse transcribed into cDNA, and the cDNA in turn becomes the template for the qPCR amplification in an experiment. The first step in gene expression analysis is RNA isolation as shown in the workflow below (Figure 1).
Gene Expression Analysis Workflow
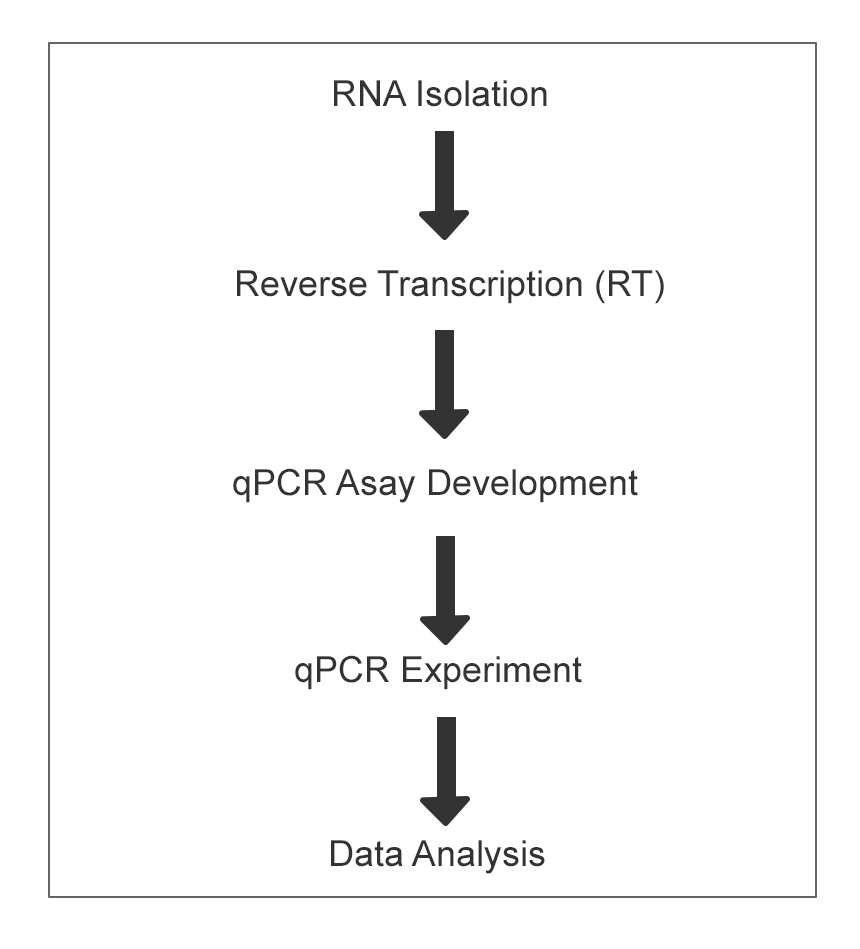
Figure 1. Steps of the gene expression analysis workflow. To learn how to isolate RNA for gene expression, review the steps listed below.
Step 1 — Sample Collection
For RNA isolation and the quantification of gene expression, harvest the samples with the appropriate kits, reagents, and instrumentation for the cell or tissue type to minimize time and maximize yield in isolating RNA.
Your sample material should be as homogeneous as possible. If your tissue sample consists of many different cell types, pinpointing the expression pattern of your target gene may be difficult. If you have a heterogeneous sample, use one of the many methods that are available for separating and isolating specific cell types, for example, tissue dissection, needle biopsies, and laser capture microdissection. The collected cells can then be used to obtain the RNA samples.
Step 2 — RNA Extraction
A good nucleic acid purification methodology will reduce protein and chemical contaminants that can partially inhibit the reverse transcription and qPCR reactions or perturb primer annealing. This can dramatically alter the Cq values producing data and interpretations that are unrelated to the tested experimental conditions.
When handling samples with a limited number of cells, an RNA extraction kit is useful. The Aurum Total RNA Isolation Kit or the SingleShot Cell Lysis RT-qPCR Kit from Bio‑Rad, assures high-quality samples with excellent purity. SingleShot can also be used to generate cell lysates suitable for RT-qPCR analysis without RNA purification. For cultured cells, yeast and bacteria, Purezol RNA Isolation Reagent is a versatile and efficient reagent for RNA, DNA and protein. Chelex 100 MB grade and Instagene from Bio-Rad can also be used for rapid RNA extraction of blood samples.
The Amplification Reagents and Plastics Brochure provides performance and ordering info on all the Bio-Rad products for RNA isolation.
See the Amplification Reagents and Plasitcs Brochure »
RNA Extraction Tips
Either total or poly(A+) RNA can be used for most real-time RT-qPCR applications. One critical consideration in working with RNA is to eliminate RNases in your solutions, consumables, and labware. Ready-to-use RNase-free solutions can be purchased, or your solutions can be treated with diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC) and then autoclaved. RNases on labware can also be inactivated by DEPC treatment or by baking at 250°C for 3 hours.
Prepared RNA samples may need DNase treatment to prevent potential amplification of any contaminating genomic DNA, which could lead to overestimation of the copy number of an mRNA. When starting material is limited, however, DNase treatment may be inadvisable, because the additional manipulation could result in loss of RNA. The amplification of potentially contaminating genomic DNA can be precluded by designing transcript-specific primers, for example, primers that span or amplify across splice junctions.
Step 3 — Analyzing RNA Quantity and Quality
Accurate RNA quantification is essential for gene expression analysis, especially when total RNA amounts are used to normalize target gene expression. RNA samples should be assessed for purity using a spectrophotometric method. RNA concentration and purity are commonly determined by measuring the ratio of UV absorbance at 260 nm and 280 nm. However, the overall sensitivity of this method is low, especially for relatively dilute samples, and it does not indicate the quality of the RNA.
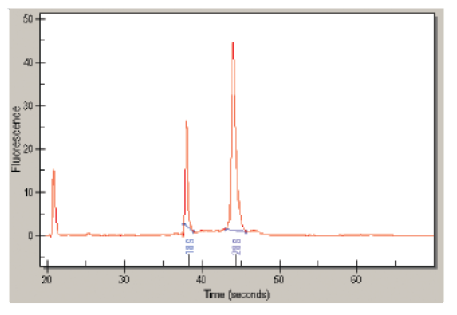
To determine RNA quality and quantity, we recommend either running a gel electrophoresis system or using a Bioanalyzer System. Examples of a high-quality total RNA preparation and a poor-quality total RNA preparation are shown in Figure 2.
-
A
-
B
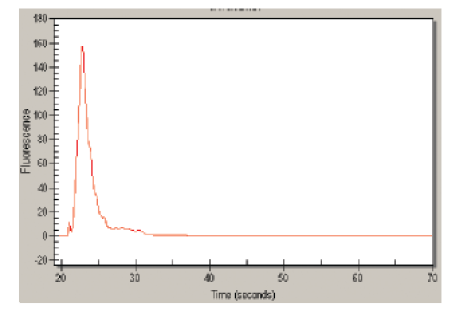
Figure 2. RNA quality assessed by an Experion Electrophoresis System. A, An example of a high-quality total RNA preparation showing distinct peaks for the 18S and 28S rRNA. B, An example of a poor-quality total RNA preparation where only small, degraded fragments are observed.
Related Products
Aurum Total RNA Mini Kit
The Aurum total RNA mini kit produces high-quality DNA-free total RNA from a wide range of starting materials, including cultured cells, bacteria, and yeast, as well as animal and plant tissues.

Aurum Total RNA 96 Kit
The Aurum total RNA 96 kit isolates high-quality DNA-free total RNA from cultured cells, bacteria, and yeast in a 96-well format for high-throughput total RNA isolation.

Aurum Total RNA Fatty and Fibrous Tissue Kit
The Aurum total RNA fatty and fibrous tissue kit produces high yields of exceptionally pure total RNA from samples that are difficult to disrupt.

PureZOL RNA Isolation Reagent
The ready-to-use PureZOL RNA isolation reagent is an efficient means of isolating RNA from a variety of sources, including cultured cell, animal and plant tissue, yeast, virus, and bacteria.

iScript RT-qPCR Sample Preparation Reagent
Bio-Rad's iScript RT-qPCR sample preparation reagent delivers efficient cell lysis and RNA stabilization for sensitive qPCR without RNA purification.
Resources

Amplification and Reagents and Plastics Brochure
An overview of PCR reagents and plastics with info on specifications, performance data, and more.

PCR Amplification Guide
A guide for RT-PCR on key concepts, experimental designs, analyses, and product recommendations.
