Activated media for ligand immobilization allow the researcher to create an affinity matrix of choice by coupling a ligand such as an antibody, enzyme, antigen, or receptor. There are multiple coupling methods. Three methods will be discussed here.
Related Topics: Affinity Chromatography, Affinity Purification of Tagged Recombinant Proteins, and Protein A/G Affinity.
Page Contents
Cyanogen bromide activation is the most common method for preparing affinity gels. It reacts with the hydroxyl groups on agarose supports to form cyanate esters and imidocarbonates. These groups react with primary amines to couple the protein onto the agarose matrix. Because cyanate esters are more reactive than are cyclic imidocarbonates, the amine will react mostly with the ester, yielding isourea derivatives, and partially with the less reactive imidocarbonate, yielding substituted imidocarbonates.
Disadvantages include the toxicity of cyanogen bromide and its sensitivity to oxidation. Cyanogen bromide activation also involves the attachment via an isourea bond, which is positively charged at neutral pH and thus unstable. Consequently, isourea derivatives may act as weak anion exchangers.

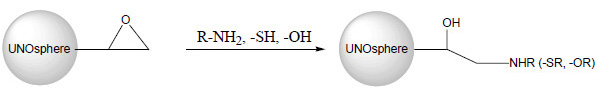
Ligands containing amino, thiol, or hydroxyl groups can be coupled to the epoxide through an epoxy ring-opening reaction under mild conditions. Following immobilization, active groups remaining on the resin need to be deactivated or blocked to avoid undesirable reaction with proteins of interest during affinity chromatography. They can be deactivated or blocked by mixing the resin with 1 M ethanolamine, pH 8–l9.
This reaction mechanism involves two steps: the activation of carboxyl groups with displacement by the nucleophile, R-NH2, thereby releasing the EDAC as a soluble urea derivative. The carboxyl groups can be present on the ligand or on the matrix. The activated carboxyl groups react with the amino groups in the reaction mixture. The illustration shows the EDAC coupling reaction for a ligand with a terminal carboxyl group to Bio-Rad’s Affi-Gel® 102 gel.

Bio-Rad's activated affinity chromatography media.
Matrix |
Functional Group |
Specificity | Capacity | Working pH | Pressure Limit |
Applications | |
| Activated Media for Spontaneous Ligand Immobilization | |||||||
| Profinity™ epoxide | Pressure-stable polymer based on UNOsphere beads | Epoxy group | Nucleophiles, amino, thiol, COOH |
36–40 mg/ml IgG | 1–14 | Up to 80 psi (5.5 bar) | Activated matrix for the immobilization of various ligands (for example, protein A, StrepTactin, and immunoglobulins) |
| Affi-Gel 10 | Crosslinked agarose |
N-hydroxy- |
–NH2 | 35 mg/ml | 3–11 | 15 psi (1 bar) | For coupling proteins with pI 6.5–11 |
| Affi-Gel 15 | Crosslinked agarose | N-hydroxy- succinimide µmol/ml ≥9 µmol/ml |
–NH2 | 35 mg/ml | 3–11 | 15 psi (1 bar) | For coupling proteins with pI <6.5 |
| Affi-Gel Hz | Crosslinked agarose | Hydrazide | Oxidized carbohydrates | 1–5 mg/ml | 2–10 | 15 psi (1 bar) | Immobilization of immunoglobulins and other glycoproteins via carbohydrate moieties |
| Affinity Media Using Carbodiimide Activation | |||||||
| Affi-Gel 102 | Crosslinked agarose | –NH2 16 ± 4 meq/ml |
–COOH | 40 mg/ml | 2–11 | 15 psi (1 bar) | Carbodiimide coupling of carboxyl-containing ligand |
There are a number of preactivated media that include dyes, metals, and other ligands. The correct choice is dictated by the group available in the ligand molecule and the nature of the binding interaction with the molecule to be purified. High selectivity and capacity make this technique ideally suited to the isolation of specific components from complex biological mixtures.
Bio-Rad's ready-to-use activated affinity chromatography media.
Matrix |
Functional Group |
Specificity | Capacity | Working pH | Pressure Limit |
Applications | |
| Ready-to-use Affinity Media | |||||||
| Affi-Gel protein A | Crosslinked agarose | Protein A 2 mg/ml |
IgG | 6–15 | 2–10 | 15 psi (1 bar) |
Purification of IgG from ascites, serum, and culture fluid; with MAPS™ buffer system; purification for 10 mg mouse IgG, per ml of media is possible |
| Affi-Prep® protein A | Pressure-stable polymer | Protein A 2 mg/ml |
IgG | 7–12 | 2–10 | 1,000 psi (70 bar) | Purifies IgG from ascites, serum, and culture fluid; pressure-stable media for process-scale applications |
| Affi-Gel Blue | Crosslinked agarose | Cibacron Blue F3GA 1.9 mg/ml | Albumin, general | ≥11 mg/ml | 2–10 | 15 psi (1 bar) |
Binds many nucleotide-requiring enzymes, albumin, and other proteins |
| DEAE Affi-Gel Blue | Crosslinked agarose | Cibacron Blue F3GA and DEAE | Albumin and serum proteins | 0.14 ml serum/ml | 2–10 | 15 psi (1 bar) |
Purifies protease-free IgG from ascites, serum, and culture fluid with minimal sample preparation |
| CM Affi-Gel Blue | Crosslinked agarose | Cibacron Blue F3GA and CM | Albumin and serum proteins | 0.17–0.5 ml serum/ml | 2–11 | 15 psi (1 bar) |
Produces albumin and protease-free antibody preparation from serum without prior dialysis |
| Affi-Prep polymyxin | Pressure-stable polymer | Polymyxin 2–4 mg/ml |
Endotoxins | >5 mg/ml | 2–10 | 1,000 psi (70 bar) | Endotoxin removal |
| Affi-Gel boronate | Polyacrylamide gel | Boronate 1.05 ± 0.15 meq/g | cis-diols | 130 µmol sorbitol/ml |
2–10 | 15 psi (1 bar) |
Adsorption of cis-hydroxyl-containing molecules, including sugars, nucleotides, and glycopeptides |
| Profinity™ IMAC | Pressure-stable polymer based on UNOsphere beads | IDA, provided charged with Ni2 and uncharged | Histidine | ≥15 mg/ml* | 2–10 | 100 psi (6.8 bar) |
Purification of recombinant proteins tagged with His; can be charged with other transition metals |
| Profinity GST** | Pressure-stable polymer based on UNOsphere beads | Immobilized glutathione | GST-tagged proteins | ≥10 mg/ml | 2–10 | 45 psi (3.1 bar) |
Purification of recombinant GST-tagged proteins |
| Profinity eXact™*** | Crosslined 6% agarose | Subtilisin protease | Subtilisin prodomain | ≥3 mg/ml tag-free protein | 2–10 | 10 psi (minus system pressure) |
Generation of native, tag-free protein by on-column purification and cleavage |
| UNOsphere SUPrA™ | Highly cross-linked polymer | Recombinant protein A | Immunoglobulins/ antibodies |
30 ± 3 mg/ml |
3–11 | 100–600 cm/hr | Purification of IgG at lab and process scale |
* Refer to bulletin 3193 for purification conditions.
** For example, Profinity GST resin is available only in prepacked cartridges.
***Profinity eXact purification resin.
